So you have to write a literature review. You find your favorite novel and then start analyzing it. This is how it’s usually done, right? It’s not. You have to learn the elements of literature review and how to deal with them.
For the starters:
Literature can be anything from a set of poems about love to serious scholarly articles about pneumonia treatment. And the word review does not mean that you have to provide a conceptual framework about these sources.
For you to find out about every crucial detail, our team created this guide on how to write a literature review. In the article, you’ll see the definition and instructions on writing the paper.
📖 What Is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a thorough review and analysis of the literature available in a chosen or given subject area. It shouldn’t just look like a chronological catalog of the sources you have found or the quotes you might find relevant.
Instead, a literature review definition shows that it:
- Locates your research focus within the context of the existing literature in the field.
- Presents your critical review of the relevant literature.
- Explains all sides of the argument.
- Evaluates the research findings and their quality.
One of the key challenges in literature review writing is establishing the research context. You should find and use works that not only relate to your field but also directly address your topic and research question. It is essential to select the sources strategically so that they highlight the research gap you aim to fill. The task becomes particularly challenging when your topic is interdisciplinary. If this sounds like your case, remember: you can always rely on our literature review writing service. PhD-level experts are here to assist you at any stage of your working process.
🎯 What Is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
When answering what the purpose of a literature review is, one needs to remember a few objectives of a literature review:
- It identifies and narrows down the problem you are studying.
- It synthesizes the information from your literature survey into a summary.
- It presents the literature in an organized way.
- It critically evaluates the available information by:
- Finding gaps in current studies.
- Showing limitations of the proposed points of view and theories.
- It provides suggestions for further research and reviews controversial areas.
What is a literature review in a research paper? It’s an overview and evaluation of what has been found, explored, and written on the topic of a given research paper.
Creating a literature review might be a part of a graduate or post-graduate work, such as a thesis or dissertation. Additionally, it can be a part of smaller academic writing pieces and research proposals.
📌 Literature Review Elements
So, what are the main features of a good literature review? You have to learn about them to write a flawless paper.
Five key elements of a literature review play an essential role:
This video will help you get more closely acquainted with the parts of the literature review:
✍️ How to Write a Literature Review
Now that you are familiar with the elements, it’s time to figure out how to write a literature review for a research paper.
Below, you will find a list of useful tips to ease your studies. And don’t forget to check out valuable links at the end of the article!
Check the Format
Before you start your paper, you need to get acquainted with the required citation style guidelines to format your literature review correctly. Here are several reasons why you need to do this first:
- To recognize the author(s) of the materials you’re using in your research.
- To give context to your study and show that your paper is properly researched.
- To enable your readers to find the sources for more detailed information if needed.
- To allow for further research by informing others about what has already been studied on a given topic.
Be sure to cite other authors’ ideas and words whenever you:
- Paraphrase.
- Make a summary.
- Quote directly.
- Use relatively unknown facts.
- Incorporate evidence that directly relates to your argument.
Choose a Topic
Selecting the right topic for your literature review is a vital step towards writing an effective paper.
The best tips for the issue are as follows:
- Look for a topic that you find interesting. The right choice will make the researching and writing process more pleasurable and rewarding in the end.
- Brainstorm your ideas. Try this method to make your ideas flow more freely. Keep refining your ideas until you find something that will pique your curiosity.
- Skim through the sources. You won’t write a literature review on this topic correctly if it hasn’t been researched by others yet. Make sure that there is enough related literature available for your review.
- Make it neither too general nor too specific. Too broad of a topic will spread your and your readers’ attention thin, and it will be challenging to study. Too narrow of an idea might be detrimental for a literature review, meaning one might not have enough supporting articles. However, if you find enough studies on a specific idea, that would be ideal.
Find Core Materials
By now, you have defined the topic and scope of your literature review. Your next step is to start identifying specific resources. Thorough academic research will undoubtedly take some time.
The good news is this:
Once it’s done the way it should be, the research almost writes the literature review for you.
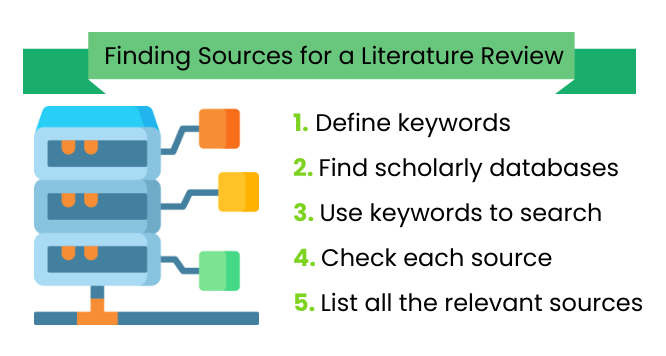
Here are some tips:
Write down any keywords that describe your topic. Use a reference tool or a thesaurus to generate this list. Then use these keywords to research scholarly databases. These search terms will help you find useful sources.
Choosing incorrect or non-descriptive keywords will return results that are too shallow.
Here are some suggestions for online multidisciplinary databases that you might use:
Evaluate the Sources
Before deciding whether you should include the material you’ve found, you should engage in a critical literature evaluation.
Why?
Some of the materials retrieved from the Internet may end up not being credible or not valuable enough for your project. Peer-reviewed journals are more likely to be scientifically valid.
You can use this table as a checklist for evaluating your sources:
Analyze the Websites
Before you use or cite any information you find on a website, you should carefully evaluate the source in a few ways:
- Search for information about the author: “About Us,” “About This Site,” etc.
- Make sure you can reach the website’s author/webmaster by e-mail or some other means.
- Assess the authority of the URL (site’s web address).
Pay special attention to top-level domains:
– .com – most likely a commercial site (maybe selling products or services).
– .edu – an educational institution (mostly reliable, but still may be a personal web page of an institution’s member).
– .gov – highly reliable, representing a government department or agent.
– .net – network access provider.
– .org – a non-profit organization (reliability level may vary).
Make a Summary
The summaries of your findings in the format of a table or concept map will help you review, manage, and summarize the literature you’ve dug up.
- If you use tables for your review, they must include an analysis to summarize, explain, and synthesize the material that you’re reviewing.
What’s the best way to create tables?
You can use Microsoft Word’s table functionality, or you can create the table in Excel first and then copy→paste/import the completed Excel sheet into Word. Using Excel will let you incorporate some useful functions like sorting your findings (e.g., by date, by author, by method, and then by date, etc.)
- You can plan your table or do the entire summary chart of your literature using a concept map. Use these services to create your maps:
- As a starting point, try organizing the following data for your literature review into tables or maps:
- Keywords and concepts.
- Points of view.
- Facts and statistics.
- Research methods.
- Research results summary, etc.
Outline and Write
Do you still think you can do without a literature review outline when translating your research into writing? You might end up having to spend too much time writing without one!
Go ahead and create an outline before you start writing your paper.
The literature review structure contains the same elements as a regular essay would:
How do you write a literature review for a research paper?
Pay special attention to these important details as well:
- Define the general problem you’re studying without making global statements.
- Somewhere at the beginning of the paper, mention why your topic is crucial.
- Make sure to highlight only the essential points from each source. And these points should refer directly to the focus of your review.
- Explain the difference between your research and that of other sources.
- Break your findings up by concepts and categories (in defense of or opposition to a particular position).
- Synthesize the materials under consideration: compare the studies, reveal their strengths and weaknesses, highlight gaps and trends in the research, etc.
- Describe the timeframe if you’re going to comment on the topic’s timeliness.
- If you need to cite a classic or landmark study, define it as it is.
- If you replicate some landmark study, point it out.
- Keep your voice front and center. Even though a literature review describes ideas from other authors, you should maintain your voice. Try to start and end the paragraph with your statements and words.
- Like any other academic paper, you should reference a few other resources when you make a point. Always back up your explanations with evidence to confirm the validity of your words.
- Comments like “no studies were found” should always be justified.
- Always give credit to authors whenever you use their ideas. And quote reasonably. Use quotes only to highlight a specific idea or fact that exemplifies your research.
- Draw conclusions about the literature that made the most significant contributions to your study area.
Now that you’ve read tips on literature review conducting and writing will be more manageable.
Helpful Links
The links below will provide you with useful literature review guidelines in different study areas. And you’ll find examples of literature reviews below!
Science
- Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- Scientific Literature Review: What it is and what it’s not (13 min video)
Medicine
- Arts in Medicine Literature Review (sample of literature review in pdf)
Sociology
Psychology literature review
- How to Write a Literature Review in Psychology
- Conducting Literature Review in Education and the Behavioral Sciences (audio tutorial)
Business and economics
- Business and Economics Literature Review
- Writing a literature review in Business and Economics
- Projects and Their Management: A Literature Review (sample in pdf)
Literature Review Topics
- Literature review: traumatic brain injury.
- Analyze the academic literature on the empowerment of youth in the UAE issue.
- Explore the literature discussing the speaker recognition process.
- Write a literature review of the articles examining the problem of digital signature.
- Cyber security of young children: a literature review.
- Examine the pertinent scholarly articles analyzing the role of an auditor in detecting fraud.
- Review the literature that discusses the connection between COVID-19 and eye diseases.
- Provide a review of the literature exploring the pros and cons of vegetarianism.
- Review the articles and studies analyzing the opioid crisis problem.
- Write the literature review on Alzheimer’s disease.
- Analyze the literature on the complication of caring for a child with ASD.
- Explore the literature discussing the problem of workplace bullying.
- Write a literature review of the articles and studies on autism spectrum disorder.
- Present a literature review on the topic of encountering the landscapes of life and death.
- Examine the literature analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of flipped classroom approach.
- Review the literature on the importance, production, and regulation of hepcidin.
- Present the literature describing the life of Native Americans in the USA.
- Analyze the literature exploring the causes and the outcomes of the Stono revolt.
- Write a review of the literature that examines the problem of substance abuse.
- Examine the literature discussing the critical traits of an effective educational leader.
- Explore the literature on human resource development issues.
- Provide a review of the literature that discusses key management skills and qualities.
- Review of the literature on evidence-based nursing practice.
- Review the literature that studies chronic fatigue.
- Analyze the articles and studies that explore the acceptability of genetic engineering.
- Write a review of studies on the legalization of physician-assisted suicide.
- Examine the literature discussing British imperialism in India.
- Provide a review of literature that describes the Civil War.
- Literature review on the ecology in art.
- Review the literature analyzing the influence of the token economy on the behavior of students with autism.
- Explore the literature studying the specifics of American football.
- Analyze the articles that examine the peculiarities of evidence-based nursing practices.
- Write a literature review on the benefits of electronic health records.
- Provide a literature review of the studies examining the challenges of single African American parents.
- Study the literature analyzing childhood obesity and ways to improve the situation.
- Literature review of the articles on breast cancer.
- Write a review of the literature studying emergency room wait time.
- Review the articles studying the importance of physical exercises for elderly people.
- Analyze the literature sources discussing the operation Jawbreaker course and outcomes.
- Review the literature on the Capstone’s PICOT question.
- Examine the academic literature researching patient fall prevention.
- Explore the literature that analyzes the ways of pressure ulcer prevention.
- Provide a review of studies examining how substance abuse results in healthcare costs for employers.
- Provide a literature review on the third culture kids issue.
- Write a literature review of academic articles discussing the strength and weaknesses of modern chronic pain management methods.
- Analyze the literature on the symptoms and treatment methods of irritable bowel syndrome.
- Examine the academic sources studying the history of autism spectrum disorder and its prevalence in different countries.
- Literature review: practice in healthcare.
- Review the papers researching anemia of chronic diseases.
- Explore the academic literature examining the role of corticosteroids in asthma treatment.
Thanks for reading the article! Now you can nail your literature review without a struggle. Share the page with peers who may need our advice.
🔗 References
- Literature Reviews: The Writing Center, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- The Literature Review A Few Tips On Conducting It Writing Advice: Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, the University of Toronto
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature: The Writing Center, the University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Literature Reviews, An Overview for Graduate Students: NC State University Libraries
- What is a Literature Review: Martyn Shuttleworth, Explorable
- The Literature Review, Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Research Guides at the University of Southern California
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review: LibGuides at University of West Florida Libraries
- Write a Literature Review: Library Guides at University of California, Santa Cruz
- Literature Reviews: LibGuides at University of Reading










![Ultimate Report Writing Tips for Students: Best Ideas [Free]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/business-desk-with-keyboard-report-graph-284x153.jpg)
